The dengue mosquito (dengue Machar) Aedes mosquito or Aedes aegypti mosquito is one of the only few types of mosquitoes that spread dengue disease. Aedes mosquitoes are visually distinctive because they have noticeable black and white markings on their body and legs. Unlike most other mosquitoes, they are active and bite only during the daytime. The peak biting periods are early in the morning and in the evening before dusk. The Aedes Aegypti life cycle depends very much on the level of feeding. Aedes Aegypti life-cycle is complex with dramatic changes in shape, function, and habitat. Female mosquitoes lay their eggs on the inner, wet walls of containers with water.
Also Read: Best mosquito killer machine
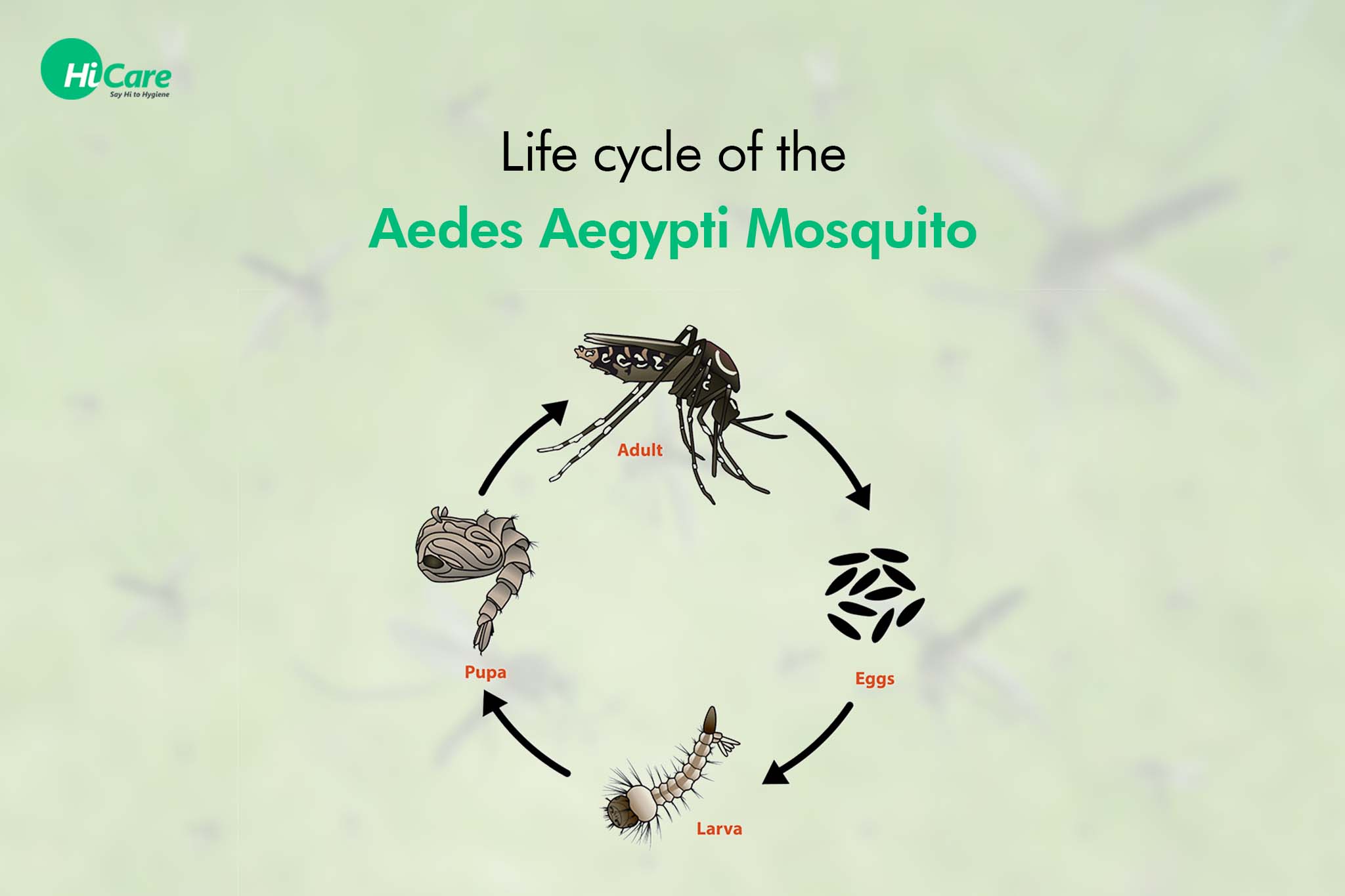
4 Stages of Life Cycle of Aedes Aegypti Mosquito
The Aedes aegypti mosquito undergoes a complete metamorphosis, which means it has four distinct stages in its life cycle. Here are the four stages:
- Egg Stage: The life cycle of Aedes mosquito begins with the female mosquito laying her eggs in stagnant water usually in containers such as buckets, flower pots or old tires. A single female mosquito can lay up to 100-200 eggs at once and can lay up to 1000 eggs over her lifetime. The eggs are very small, black or brown and can stick to the sides of the container.
- Larva Stage: After the eggs are laid they hatch into larvae within 2-3 days. The larvae are small, worm-like creatures that live in the water and feed on organic matter such as algae and bacteria. The larvae have a distinctive head with mouth brushes for feeding and a thorax and abdomen with several segments. The larvae go through four molts or stages, during which they shed their skin and grow larger. The larval stage lasts for about 4-14 days, depending on the temperature and availability of food.
- Pupa Stage: After the fourth molt the larvae enter the pupa stage. The pupa is a non feeding, comma shaped creature that is also found in the water. During this stage, the mosquito undergoes a metamorphosis, transforming into an adult mosquito. The pupal stage lasts for about 1-4 days. After which the adult mosquito emerges from the pupal case.
- Adult Stage: The adult Aedes Aegypti mosquito emerges from the pupal case and rests on the surface of the water until its wings are dry. The adult mosquito is about 6 mm in length and has a dark brown or black body with white stripes on its legs and thorax. The female mosquito needs a blood meal in order to develop her eggs and will seek out a host such as a human or animal to bite. After taking a blood meal the female mosquito will lay her eggs in a water container and the life cycle of aedes mosquito starts all over again.
Also Read: Disadvantages of mosquito repellent
Necessary Time for Mosquito Eggs to Become Adults
The eggs of Aedes mosquito can lie dormant in dry conditions for up to about nine months, after which they can hatch if exposed to favourable conditions, i.e. water and food. Aedes mosquito life cycle begins with the larvae hatching when water inundates the eggs as a product of rains or the addition of water by people. In the following days, the larvae will feed on microorganisms and particulate organic matter, shedding their skins three times to be able to nurture from first to fourth instars. Pupae do not feed; they just change in form until the body of the adult, flying mosquito is formed. Then, the newly formed adult emerges from the water after breaking the pupal skin.
The total Aedes aegypti life cycle lasts 8-10 days at room temperature, depending on the level of feeding
Life Span of Aedes Aegypti or Dengue Mosquitoes
The adult Aedes Aegypti life cycle can range from two weeks to a month depending on ecological conditions.
Biological Details of Dengue Mosquitoes
Male mosquitoes are slightly smaller in size compared to female mosquitoes and the female mosquitoes feed on blood because the protein in the blood helps them develop the eggs. Mosquitoes are attracted to heat and lactic acid and tend to bite people who have just exercised, bigger people attract mosquitoes more because they produce higher carbon dioxide & lactic acid. Female dengue mosquito lays about 300 eggs at one time The mosquito becomes infective approximately seven days after it has bitten a person carrying the virus. This is the extrinsic incubation period, during which time the virus replicates in the mosquito and reaches the salivary glands.
Habitat of Dengue Mosquitoes
Dengue mosquitoes or Aedes mosquito have unusual breeding sites frequently found in domestic containers, flower pot plates/trays, ornamental containers. They also hide and breed in toilet bowls, closed perimeter drains and gully traps, AC vents, water coolers. Any place where water gets accumulated and stays stagnant for over few days becomes a breeding ground for these Aedes mosquitoes. Do a quick check of your home and bungalow to identify any potential breeding spots in monsoon season.
What Attracts Dengue Mosquitoes
According to a new experiment the presences of flowers have known to have an effect on egg-laying behavior as mosquitoes drink nectar from flowers. The carbon dioxide we exhale and the sweat we generate is what attracts mosquitoes. When it combines with the bacteria making us vulnerable to the mosquitoes. When it comes to the blood type as well, mosquitoes have a peculiar taste to a specific blood group. Studies have shown that mosquitoes are most attracted to Type O blood and least attracted to Type A. Mosquitoes are also more attracted to people with a greater build-up of lactic acid on their skin.
10 Tips on How to Get Rid of Dengue Mosquitos (Aedes Mosquitos)
Getting rid of dengue mosquitoes (Aedes mosquitoes) involves taking preventive measures to reduce their breeding sites and using control methods to minimize their population. Here are some steps you can follow:
- Eliminate Breeding Sites: Aedes mosquitoes breed in stagnant water. Regularly inspect your surroundings and remove any potential breeding grounds such as discarded containers, old tires, flower pots, and other items that can collect rainwater.
- Clean Gutters and Drains: Keep gutters and drains free from debris and ensure that water flows freely through them to prevent water pooling.
- Use Mosquito Nets: When sleeping, especially during the day (since Aedes mosquitoes are active during the day), use mosquito nets to protect yourself from mosquito bites.
- Wear Protective Clothing: When going outside, wear long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and use mosquito repellent on exposed skin.
- Use Mosquito Repellents: Apply mosquito repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus on exposed skin. Follow the instructions on the product for safe usage.
- Install Screens: Use window and door screens to keep mosquitoes out of your home.
- Mosquito Traps: Consider using mosquito traps that use ultraviolet light or other attractants to lure and trap mosquitoes.
- Biological Control: In some areas, introducing natural predators of mosquitoes, like certain fish or dragonflies, can help control their population.
- Insecticides: If the mosquito population is particularly high, you can use insecticides to control them. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use approved insecticides.
- Seek Professional Help: If you’re unable to control the mosquito population on your own, consider contacting a pest control professional or your local health department for assistance.
Conclusion
It is, therefore, necessary to have regular pest control services in your home and make sure to hire an expert for mosquito control service.
Frequently Asked Questions about Mosquitos
What is the life cycle or lifespan of dengue mosquito?
Dengue mosquito lifespan is around one month including stages of being an egg, larvae, pupae and adult mosquito.
What diseases does Aedes Aegypti mosquito transmits?
Aedes Aegypti mosquito is known to transmit several deadly diseases including Dengue fever, Zika virus, Chikungunya, Yellow fever and West Nile virus.
In what regions Aedes Aegypti mosquito mostly found?
Aedes Aegypti mosquito is primarily found in tropical and subtropical regions of the world. However, due to increased global travel and trade, Aedes Aegypti mosquito has also been found in Southeast Asia, Central and South America, Africa and the Caribbean regions.
Why does dengue mosquito bite in daytime?
Dengue mosquitoes, also known as the Aedes Aegypti mosquitoes, generally bite during the daytime because they are diurnal, which means they are most active during the daytime.
What attracts the Aedes Aegypti mosquitos?
Aedes mosquitoes are attracted to their carriers by the carbon dioxide that is exhaled by humans and animals, body heat, and certain scents. They tend to seek their hosts during the day when people are more active, which gives them more chances to find a host.